Laboratory Experiment - 6
6. Apply HTML, CSS and JavaScript to design a simple calculator to perform the following operations: sum, product, difference, remainder, quotient, power, square-root and square.
HTML Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<metacharset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>SimpleCalculator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style1.css">
</head>
<body>
<divclass="calculator">
<h1>Simple Calculator</h1>
<div>
<input type="number" id="number1" placeholder="Enter first number">
</div>
<div>
<input type="number" id="number2" placeholder="Enter second number (optional)">
</div>
<div>
<button onclick="calculate('sum')">Sum</button>
<button onclick="calculate('difference')">Difference</button>
<button onclick="calculate('product')">Product</button>
<button onclick="calculate('quotient')">Quotient</button>
<button onclick="calculate('remainder')">Remainder</button>
<button onclick="calculate('power')">Power</button>
<button onclick="calculate('square')">Square</button>
<button onclick="calculate('sqrt')">Square Root</button>
</div>
<h2>Result: <span id="result">0</span></h2>
</div>
<script src="script1.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
CSS Code:
body {
font-family:Arial, sans-serif;
background-color:#f0f0f0;
display:flex;
justify-content:center;
align-items:center;
height:100vh;
margin:0;
}
.calculator {
background-color:#fff;
padding:20px;
border-radius:10px;
box-shadow:0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align:center;
}
.calculator h1 {
margin-bottom:20px;
}
input[type="number"] {
width:200px;
padding:10px;
margin:10px 0;
font-size:16px;
}
button {
padding:10px 15px;
margin:5px;
font-size:16px;
cursor:pointer;
border:none;
background-color:#007bff;
color:white;
border-radius:5px;
}
button:hover {
background-color:#0056b3;
}
#result {
font-size:24px;
font-weight:bold;
}
Java Script Code:
function calculate(operation){
const num1 = parseFloat(document.getElementById('number1').value);
const num2 = parseFloat(document.getElementById('number2').value);
let result = 0;
switch (operation) {
case 'sum':
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case 'difference':
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case 'product':
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case 'quotient':
result = num1 / num2;
break;
case 'remainder':
result = num1 % num2;
break;
case 'power':
result = Math.pow(num1, num2);
break;
case 'square':
result = num1 * num1;
break;
case 'sqrt':
result = Math.sqrt(num1);
break;
default:
result = 0;
}
document.getElementById('result').innerText = result;
}
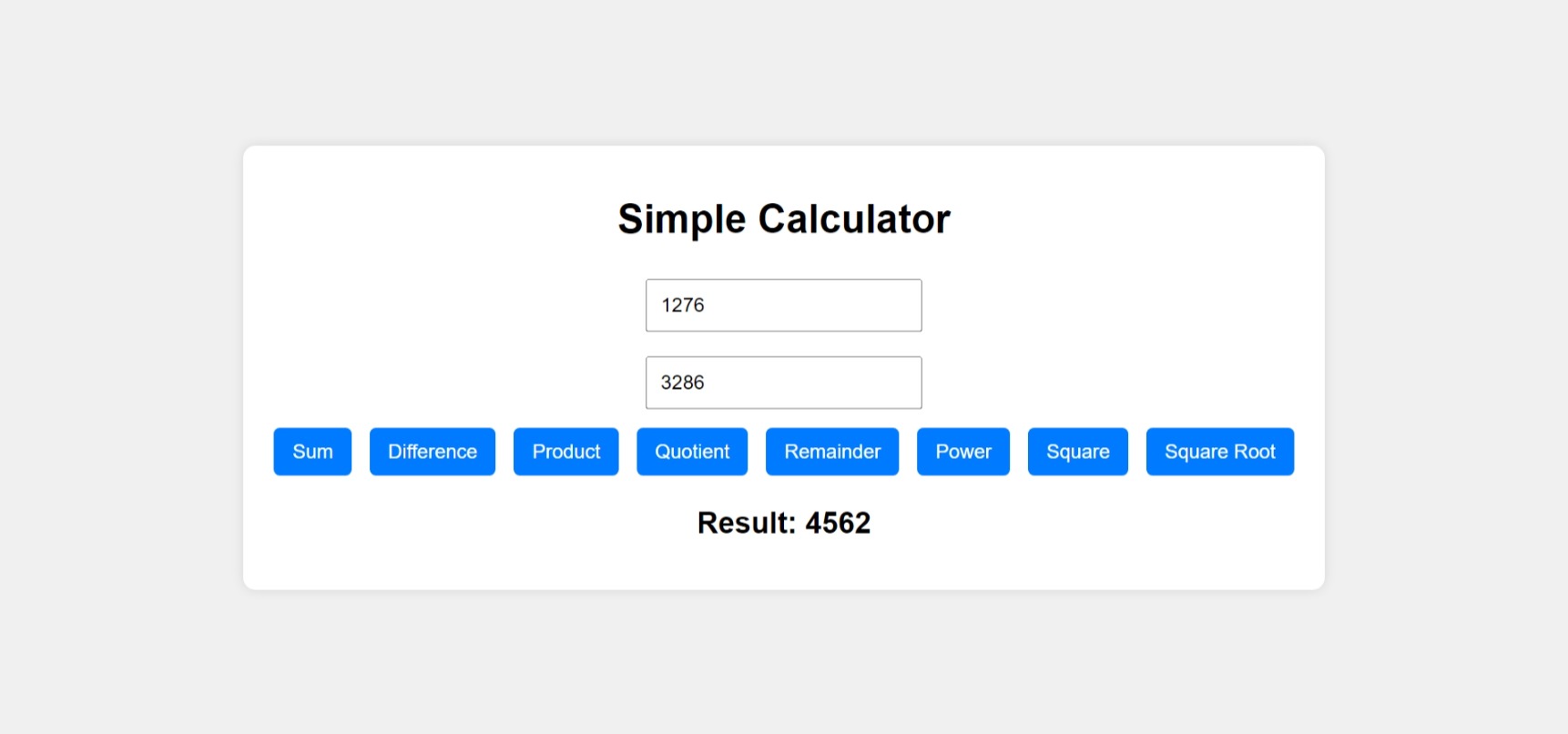
Output:
Explanation of Code:
HTML:
- A simple form with two input fields for the user to enter numbers.
- Buttons are created for different operations (sum, difference, product, quotient, remainder, power, square, square-root).
- Results are displayed inside a
<span>element with the IDresult.
CSS:
- Styling is applied to the calculator to make it visually appealing. The layout is centered using Flexbox.
- Buttons are styled to change colors when hovered.
JavaScript:
- The
calculate()function handles the mathematical operations based on the button clicked. - It retrieves the values from the input fields, performs the selected operation, and displays the result.
1. Q: What is the purpose of parseFloat() in
JavaScript?
A: parseFloat() converts a string or value to a floating-point number,
allowing us to handle both integers and decimal numbers in the calculator.
2. Q: What does the switch statement do in the
calculator's JavaScript code?
A: The switch statement evaluates the operation parameter and executes
the corresponding block of code based on which button was clicked.
3. Q: How do we calculate the square of a number
using JavaScript?
A: The square is calculated using num1 * num1, which multiplies the
number by itself.
4. Q: What function is used to calculate the square
root of a number in JavaScript?
A: The Math.sqrt() function is used to calculate the square root of a
number.
5. Q: Why do we use innerText in JavaScript?
A: innerText is used to change the text content of an HTML element. In
this case, it updates the result of the calculator operations.
6. Q: How does the onclick attribute work in HTML
buttons?
A: The onclick attribute specifies a JavaScript function to run when the
button is clicked.
7. Q: What is the role of the Math.pow() function in
this calculator?
A: The Math.pow() function is used to calculate one number raised to the
power of another (exponentiation).
8. Q: What happens if you try to divide a number by
zero in JavaScript?
A: In JavaScript, dividing by zero results in Infinity.
9. Q: What is NaN in JavaScript and when can it
occur?
A: NaN stands for "Not-a-Number" and occurs when a
mathematical operation cannot return a valid number (e.g., trying to divide a
string by a number).
10. Q: How do you handle missing inputs in the
calculator?
A: You can check if the input fields are empty using JavaScript before
performing any operation and display an error message or prevent calculation.
11. Q: What does the id attribute do in HTML?
A: The id attribute uniquely identifies an HTML element so it can be
referenced in CSS or JavaScript.
12. Q: What is Flexbox and why is it used in the CSS
code?
A: Flexbox is a CSS layout model that allows easy alignment and
distribution of elements. It’s used here to center the calculator on the
screen.
13. Q: What is the purpose of the placeholder
attribute in input fields?
A: The placeholder attribute provides a hint or example text inside an
input field to guide the user on what to enter.
14. Q: Why is the button:hover style used in the CSS
code?
A: The button:hover style changes the appearance of the button when the
user hovers over it, improving user interaction feedback.
15. Q: What does the text-align: center CSS property
do?
A: It centers the text horizontally within its containing element.
16. Q: How is the square of a number calculated in
the calculator?
A: The square is calculated using num1 * num1 when the
"Square" button is clicked.
17. Q: What is the role of the Math.sqrt() function
in the code?
A: It calculates the square root of the input number.
18. Q: How can you style buttons to change color when
clicked?
A: You can use the :active pseudo-class in CSS to change the button
color when it is clicked.
19. Q: What is the role of the value attribute in
input elements?
A: The value attribute holds the current value of the input field that
can be retrieved and used in JavaScript.
20. Q: How do you update the result in the HTML using
JavaScript?
A: The result is updated using document.getElementById('result').innerText,
which changes the text content of the result <span>.
Comments
Post a Comment